Washing machine power - how many kW does it consume?
 The power of the machine may vary. And in order to determine the number of kW that your household appliance uses, you can check the sticker. The one that is on its body. The sticker may contain this information. You can also find out by specifying which energy class of washing machines applies to your model. Let's discuss this issue in more detail.
The power of the machine may vary. And in order to determine the number of kW that your household appliance uses, you can check the sticker. The one that is on its body. The sticker may contain this information. You can also find out by specifying which energy class of washing machines applies to your model. Let's discuss this issue in more detail.
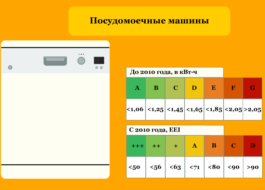
Electricity consumption classes
All washing machines are divided into classes according to their efficiency in electricity consumption. Those classes that are more economical are designated in the form of the Latin letter “A”. The “+” sign(s) can also be added to it. These signs will tell us about even more modest consumption. The highest and most economical designation is “A++”. The least economical is “G”.
Typically, icons that indicate the class of household appliances, be it a refrigerator, washing machine or other large units, are placed on stickers. Those located on the body. You can also find them in the detailed description of your machine on the manufacturer’s website.
The amount of kWh per kilogram of laundry washed is calculated in laboratory conditions. After which various models of household appliances are assigned one or another energy consumption class.
How many kW per hour do different classes of washing machines use?
- Let's start with the most economical option. Class “A++” requires the minimum amount of energy. Such machines require less than 0.15 kWh per kilogram of laundry.
- Next comes "A+". A washing unit with this marking will need less than 0.17 kW/h per 1 kg of washed items.
- The letter “A” means that electricity consumption will be in the range from 0.17 to 0.19 kW/h per kg of laundry.
- For a machine with the designation “B” you will need 0.19-0.23 kW/h/kg.
- For class “C”, 0.23 to 0.27 kW/h per kg of laundry will be sufficient.
- A machine marked “D” will require from 0.27 to 0.31 kWh per kg of items.
- There is no point in listing the remaining options in detail. Since modern household washing machines do not use them. We can only mention that they will require more than 0.31 kW/h/kg.
For laboratory tests, it is customary to wash at 60 degrees. And cotton items are used as laundry. The drum is loaded with the maximum permitted amount of laundry. All calculations that lead to determining the energy efficiency class are based on such a wash.
As you understand, a different amount of kW can be used in a real wash. Since items may be made of a different material, the temperature and washing conditions may also be different.
What else can affect the number of kilowatts consumed by the machine?
It should also be noted that the following factors also influence the actual amount of energy consumed. And more specifically:
- The program selected for washing clothes. It may differ in heating temperature, duration, intensity, number of engine revolutions during spinning, presence/absence of additional options (for example, adding a second rinse), etc.
- The type of fabric from which the washed items are made also matters. Because different fabrics may have different weights when dry and wet. In addition, it may require different washing cycles.
- In addition to the above, it can affect the number of kW and how loaded the washing machine drum is.
How much electricity is needed for other household appliances?
Below we present a table showing the average power consumption values of various household electrical appliances that can be used at home.
| Type of electrical appliance | Power consumption |
| Cooking surface | From 1 to 2 kW. |
| Kitchen hood | From 0.12 to 0.24 kW. |
| Water heater up to 150 liters | Approximately equal to 6 kW. |
| Household air conditioner | 0.4 – 0.24 kW. |
| Microwave | 0.6 – 2 kW. |
| Mixer | About 0.2 kW. |
| Home vacuum cleaner | Approximately 1kW. |
| Dryer | 2-3kW. |
| Desktop computer | 0.3-1kW. |
| Dishwasher | About 3kW. |
| TV is normal | 0.15kW. |
| Iron | 1kW. |
| Fridge | 0.2kW. |
| Electric stove | 3-8kW. |
| Electric grill | 1-3.6 kW. |
| Toaster | 0.8-1.5 kW. |
| Pressure cooker | From 1 to 2 kW. |
| Built-in oven | From 2 to 5 kW. |
| Coffee machine | From 0.5 to 1 kW. |
| Instantaneous water heater | About 3.5 kW. |
| Freezer | About 0.2 kW. |
Interesting:
3 reader comments



















Electricity is measured not in kWh, but in kWh.
Power in terms of class is not what is written in the article. In this case, it is described how many kilowatts the washing machine will transfer to the electricity meter, multiplying this by the amount of the tariff you will find out how much in monetary terms you will spend per hour of washing. The power of the washing machine itself ranges from 1.5 to 2 kW on average. Let’s say for a heating element from 1.2 kW, a pump from 24 to 0.5 kW, and a motor that rotates the drum.We sum all this up and get the power at which we can calculate the cross-section of the wire and the circuit breaker in the panel. And class A, A++, etc. is the average number of kW spent on washing at 60°.
Super! Everything I wanted to find was found only thanks to your answer! Otherwise there is water everywhere, there is no answer anywhere. I need power just to select the section of the extension cord.